α-helix is spiral in shape and has a rigid arrangement of polypeptide chain as proposed by Pauling and Corey (1981). The salient features of α-helix are as follows:
- The α-helix structure contains amino acids extending outwards from the central axis.
- The α-helix structure is stabilised by the hydrogen bonding formed between the H atom attached to peptide N and O atom attached to peptide C. They are individually weak but together they are strong to stabilise the helix.
- All amino acids, except the first and last ones, are involved in hydrogen bonding.
- A single α-helix turn contains 3.6 amino acids and the distance covered by this is 0.54 nm. The space between each amino acid is 0.15 nm.
- Low energy is utilised for the α-helix formation.
- The stability is more for the α-helix than for the left-handed helix.
- Proline is the only amino acid that disrupts the α-helix.
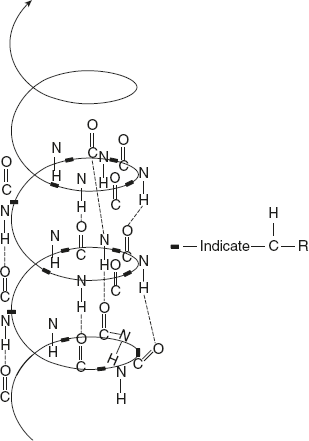
Figure 3.5 Structure of α-helix
Leave a Reply