Drugs may be injected into almost any organ or area of the body, including the joints (intra-articular), joint fluid area (intrasynovial), spinal column (intraspinal), spinal fluid (intrathecal), arteries (intra-arterial), heart (intracardiac; in an emergency), into a vein (intravenous), into a muscle (intramuscular), into the skin (intradermal, intracutaneous), or under the skin (subcutaneous, hypodermic) (Fig. 8.1).
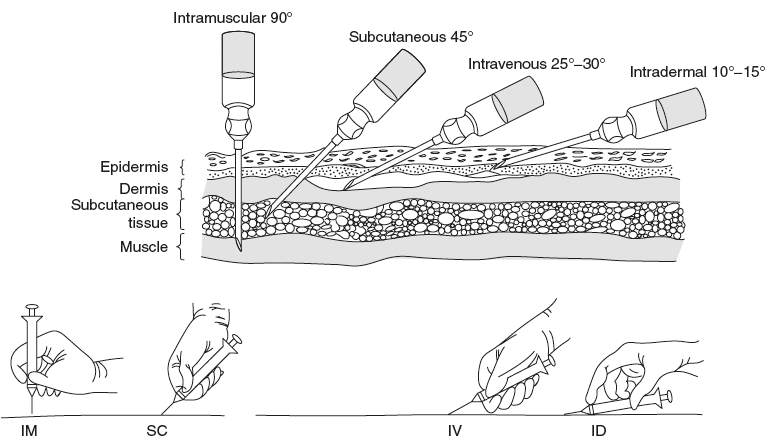
Figure 8.1 Different Sites of Injection Administration
Leave a Reply