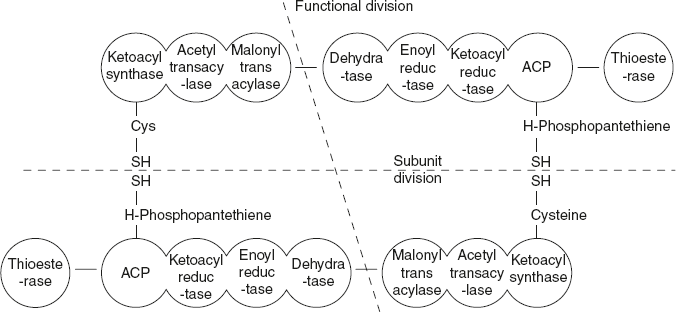
Fatty acid synthase is a dimmer composed of two identical subunits (monomers), each with a molecular weight of 240,000. Each subunit contains the activities of seven enzymes of FAS an ACP (acyl-carrier protein) with 4′-phosphopantothiene SH group. The two subunits lie in anti-parallel (head to tail) orientation. The SH group of phosphopantetheine of one subunit is in close proximity to the SH group of cysteine residue (of the enzyme ketoacyl synthase) of the other subunit.
Each monomer of FAS contains all the enzyme activities of fatty acid synthesis. But only dimer is functionally active. This is because the functional unit consists of half of each subunit interacting with the complementary half of the other. Thus, the FAS structures have both functional division and subunit division. The two functional subunits of FAS independently operate and synthesise two fatty acids simultaneously.
Leave a Reply