A microsomal enzyme system called fatty acyl-CoA desaturase is responsible for the formation of unsaturated fatty acids. This reaction also involves flavin-dependent cytochrome b5 reductase NADH and O2. The monounsaturated fatty acids, namely oleic and palmitoleic acids, are synthesised from stearic acid and palmitic acid, respectively. Mammals lack the ability to introduce double bond in fatty acid between carbons 9 and 10. Hence linoleic acid – 18: 2, 9, 12 and linolenic acid – 18: 3; 9, 12, 15 are essential for a man in diet.
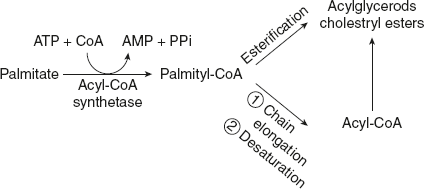
Fate of palmitate after biosynthesis is shown below
Leave a Reply