ELECTRON CARRIERS
Electron carriers in the electron transport chain are the following:
- NAD+ and NADP+
- FAD and FMN
- Q, CoQ, or ubiquinone
- Cytochromes – b, c, a
- NAD+ and NADP+Nicotinamide nucleotide linked dehydrogenase catalyse reversible reactions of the following general types:Reduced substrate + NAD+
 Oxidised substrate + NADH+ H+
Oxidised substrate + NADH+ H+
Reduced substrate + NADP+ Oxidised substrate + NADP+ H+NAD–linked dehydrogenase dehydrogenates two hydrogen atoms from their substrates. One of the atoms is transferred in the form of a hydride ion (H− is the equivalent of a proton and two electrons) to NAD+ and NADP+. The second hydrogen atom is released as H+ in the medium. The reduced form of NAD+ or NADP+ converts the nicotinamide benzene ring (with a fixed charge of the ring nitrogen) to the quinonoid form (with no charge on the nitrogen ring).Some important reactions catalysed by NAD+ and NADP+ dehydrogenase:ReactionLocationNAD-linked reactions: A – KG + CoA + NAD+
Oxidised substrate + NADP+ H+NAD–linked dehydrogenase dehydrogenates two hydrogen atoms from their substrates. One of the atoms is transferred in the form of a hydride ion (H− is the equivalent of a proton and two electrons) to NAD+ and NADP+. The second hydrogen atom is released as H+ in the medium. The reduced form of NAD+ or NADP+ converts the nicotinamide benzene ring (with a fixed charge of the ring nitrogen) to the quinonoid form (with no charge on the nitrogen ring).Some important reactions catalysed by NAD+ and NADP+ dehydrogenase:ReactionLocationNAD-linked reactions: A – KG + CoA + NAD+  Succinyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H + Mitochondria
Succinyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H + Mitochondria
Malate + NAD+ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H + Mitochondria and cytosol
Oxaloacetate + NADH + H + Mitochondria and cytosol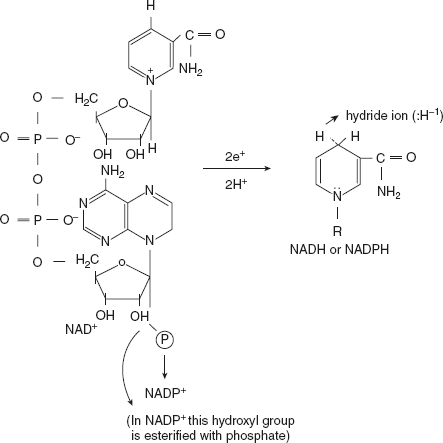
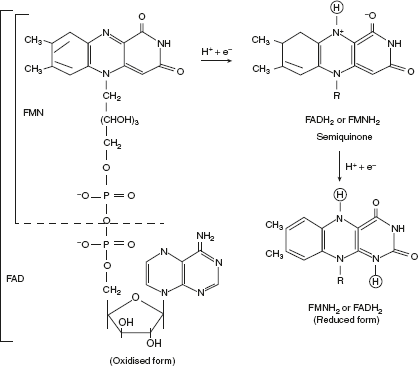
- FlavoproteinsFlavoproteins contain a very tightly, sometimes covalently bound flavin nucleoticle either FMH or FAD. The oxidised flavin nucleotide can accept either one electron (H+ and e−) yielding semiquinone form (FADH•, FADH•) or two electrons (2H+ and 2e−) yielding FADH2 or FMNH2.
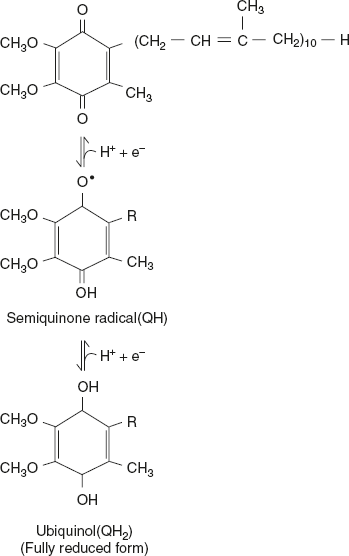
- Ubiquinone CoQ or QUbiquinone is a lipid-soluble benzoquinone with a long isoprenoid side chain. The role of ubiquinone in the electron transport chain is that it will accept one electron to become semiquinone (QH) or two electrons to form ubiquinol (QH2). As ubiquinone is small and hydrophobic in nature, it is freely diffusible within the lipid bilayer of inner mitochondrial membrane and can shuttle, reducing equivalents between less-mobile electron carriers in the membrane. Since it carries both electrons and protons, it plays a central role in coupling electron flow to proton movement.
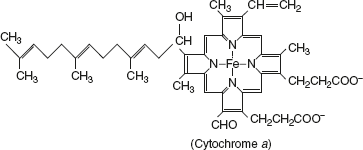
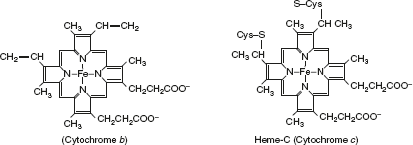
- CytochromesCytochromes are proteins in nature and have a characteristic strong absorption of visible light, due to the presence of iron-containing heme prosthetic groups. Mitochondria contain three classes of cytochromes designated as a, b, and c, distinguished by their light-absorption spectra: a-600 nm, b-560 nm, and c-550 nm. The heme cofactors of a and b cytochromes are tightly, but not covalently, bound to their associated proteins; the heme c type cytochromes are covalently attached through cys residues.
Leave a Reply