Lecithin is readily hydrolysed by boiling with acid and alkalis. Lecithin is hydrolysed by enzymes called lecithinase. There are four different types of lecithinase occur in nature: lecithinase A, lecithinase B, lecithinase C, and lecithinase D.
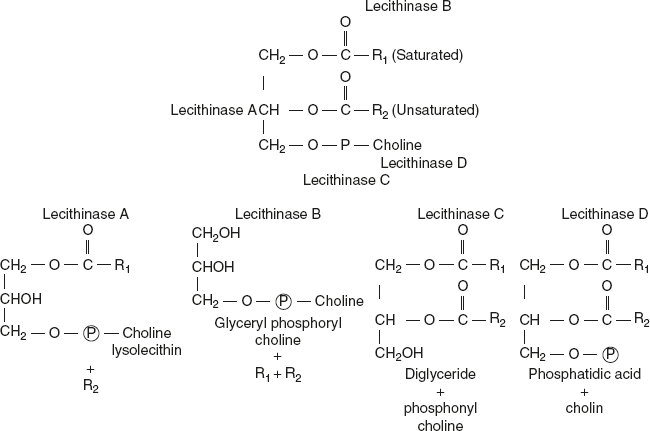
Lecithinase A is found in cobra venom. It is also present in spider venom and poisonous stings. Lecithinase A action is specific; it acts only on the unsaturated fatty acid. Lysolecithin is a powerful haemolytic poison which causes haemolysis of erythrocytes.
Lecithinase B is present in pancreas. It hydrolyses both the saturated and unsaturated fatty acids from lecithin, leaving behind glyceryl phosphoryl choline.
Lecithinase C is found in plants. It hydrolyses lecithin at the point between glycerol and phosphoric acid with the liberation of diglyceride and phosphoryl choline.
Lecithinase D is found in leafy vegetables like cabbage. It hydrolyses the lecithin into choline and phosphatidic acid.
Lecithin forms stable compounds with proteins, carbohydrates, and heavy metals. During absorption of fat, the lecithin content of blood increases as the blood lipids increase.
Leave a Reply