Explanation
Mutarotation means changing of optical rotation. Tamet explained that when a solution of freshly prepared crystalline glucose of α-D-form is observed in a polariscope, its initial specific rotation ![]() of +121.1° gradually decreases and finally becomes steady at
of +121.1° gradually decreases and finally becomes steady at ![]() + 52.5°.
+ 52.5°.
If, however, a solution of pure crystals of β-D-glucose is observed in a polariscope, the initial specific rotation of ![]() + 19°. For β-D-glucose gradually increases and finally becomes steady at + 52.5°.
+ 19°. For β-D-glucose gradually increases and finally becomes steady at + 52.5°.
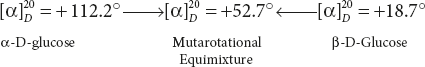
All reducing sugars (except a few ketoses) undergo mutarotation.
Leave a Reply