- Chromosomal DNA is made up of long DNA molecules with the size MW 1.6 × 106 to 2 × 109.
- A DNA polymer generally contains 1010 deoxynucleotides.
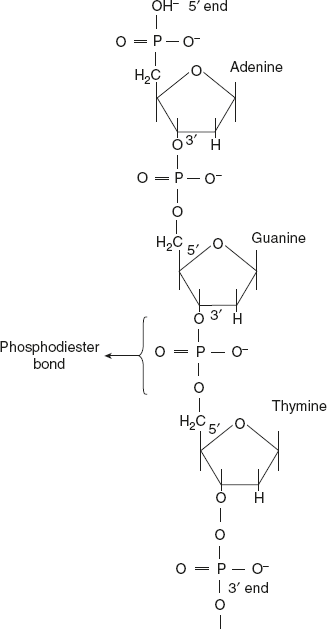
- The four different types of bases that are present in the DNA molecules are adenine deoxynucleotides (dA), thymine deoxynucleotides (dT), guanine deoxynucleotides (dG), and cytosine deoxynucleotides (dC).
- Nucleotides are connected to one another by covalent 3′-5′-phosphodiester linkage. The ester linkage of a single phosphate residue is with the 3′—OH of one nucleotide with 5′—OH group of ribose of the next molecule.
- Phosphodiester linkage gives rise to a linear polydeoxynucleotide strand with two free ends on both sides.
- Each strand has one free 5′phosphate group without phosphodiester linkage at one end, which is called the 5′ end. The opposite group is called the 3′ end.
- The primary structure mainly consists of different deoxynucleotides in one strand joined together by phosphodiester linkages.
- The backbone of the primary structure is sugar phosphate residues, while the purine and pyrimidine bases connected with the sugar residue project laterally from the backbone.
Leave a Reply