Oxygen atoms are often involved in the bonds of both alkali metal and alkaline earth metal cations, bonds of the latter being relatively stronger. Mg2+ is accumulated by cells in exchange for transport of Ca2+ in the opposite direction. So Ca++ activation enzymes are mostly extracellular ones. Example: Salivary and pancreatic α-amylases.
Intracellular enzymes require Mg2+ for activity, and in most cases, this requirement can be replaced in vitro by one for Mn2+. Example: Arginase –M2+.
For Mg2+. Example: Muscle creatine kinase.
Creatine + MgATP ![]() MgADP + Phosphocreatine + H+
MgADP + Phosphocreatine + H+
The true substrate is MgATP, and the reaction proceeds via the formation of the complex creatine E ATP Mg. Cohen and colleagues showed that divalent cation binds to α and β phosphate of nucleotide, but not in the terminal γ-phosphate, which is transferred to creative.
In contrast, the reaction catalysed by pyruvate kinase involves a cyclic metal bridge complex.
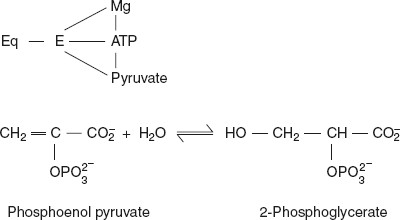
Enolase is a dimeric enzyme, having two Mg2+ ions that are needed to stabilise the active dimer. In addition, two more Mg2+ ions are required if each of two sites binds to a substrate.
Leave a Reply