Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the universal currency of free energy in biological systems; living objects require a continuous supply of free energy mainly for the following four purposes:
- To synthesize macromolecules from simpler and smaller precursors.
- To transport of molecules and ions across membranes against gradients.
- To perform mechanical work, as in muscle contraction.
- To ensure fidelity of information transfer.
The free energy in these processes is derived from the environment. Autotrophs obtain this energy by trapping light energy from the sun. On the other hand, heterotrophs obtain it by oxidation of foodstuffs in the form of organic material present in other organisms, living or dead, before it is used for biosynthesis, transport, motion, and fidelity.
ATP plays a major role in the transfer of free energy from exergonic (energy yielding) to endergonic (energy requiring) reaction in almost all the cells. Karl Lohmann discovered ATP in the extracts of skeletal muscles. In 1941, Fritz Lipmann postulated that ATP is the primary and universal carrier of chemical energy in cells. He also postulated the ATP cycle. ATP and its successive hydrolysis products ADP and AMP are nucleotides consisting of adenine, ribose, and 3, 2, 1 phosphate groups, respectively. ATP occurs not only in cell cytosol but also in mitochondria and nucleus as shown in Figure 7.1.
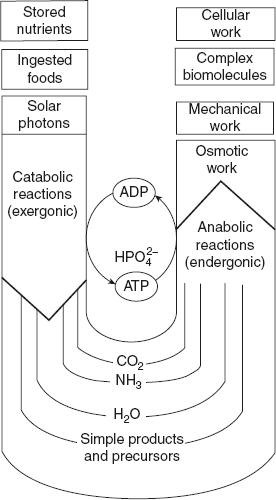
Figure 7.1 The ATP Cycle
At pH 7.0, the phosphate groups of ATP, ADP, and AMP are almost fully ionised so that they occur as multiple charged anions ATP4−, ADP3−, and ADP2−. But as the cell fluid contains high concentrations of Mg2+, both ATP and ADP exist largely as Mg ATP2− and Mg ADP− complexes.
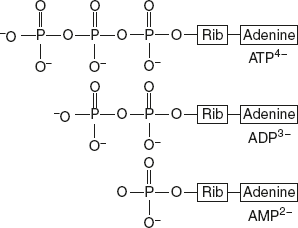
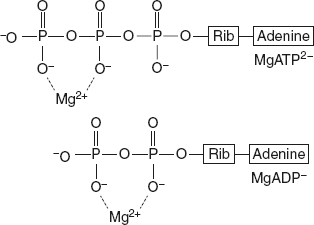
ATP plays a major role in the transfer of free energy in the systems rather than in the storage of energy. In a cell, an ATP molecule is consumed within a minute of its production. The turnover of ATP is usually high. For example, a human body consumes 40 kg/day. During strenuous exercise, the rate of consumption is 0.5 kg/minute. The free energy change for ATP is large and negative.
Leave a Reply