Source
Calcium sennosides are calcium salts of sennosides A and B obtained from the leaves and pods of Cassia angustifolia and Cassia acutifolia. Known in commerce as Indian and Alexandrian Senna these plants have been used as natural, safe, time-tested laxatives in traditional as well as modern systems of medicine. In India, senna is extensively cultivated in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat and is an important plant drug exported from India.
Despite the availability of a number of synthetic as well as natural laxatives, sennosides remain among the most extensively used drugs for both habitual constipation and occasional use. Senna is listed in the World Health Organization’s (WHO) list of essential medicines.
Sennosides A and B were first reported by Stoll in 1941 and they are present in greater concentration than other sennosides namely C, D, E, F and G.
Senna leaf suitable for medicinal use should contain not less than 2% dianthrone glycosides calculated in terms of sennoside B. Sennoside content varies from 1.2% to 2.5% in Indian senna and from about 2.5% to 4.5% in Alexandrian senna. Senna preparations in the form of powdered leaf, powdered fruit or extracts are typically standardized to a given sennoside content. Sennosides are isolated from senna as calcium salts as they are better absorbed gastrointestinally.
Uses
Senna is a stimulant laxative and acts on the wall of the large intestine, increasing peristaltic movement. After oral administration, the sennosides are transformed by intestinal flora into rhein anthrone which appears to be the ultimate purgative principle. The glycoside residues in the active constituents are necessary for water solubility and subsequent transportation to the site of action.
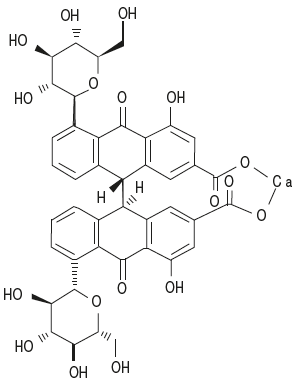
Description
Sennosides are dimeric hydroxyanthraquinone glycosides chemically designated as 5,5′-bis(beta-D-gulcopyranosyloxy)-9,9′,10,10′-tetrahydro-4,4′-dihydroxy-10,10′-dioxo[9,9′-bianthracene]-2,2′-dicarboxylic acid. With a molecular formula of C42H36CaO18, calcium sennosides occur as pale brownish hygroscopic powder, soluble in water and alcohol.
Sennosides A and B are a pair of stereoisomers containing rhein dianthrone (sennidin A and B) as the aglycone. Minor constituents of senna include sennosides C and D, which are also a pair of optical isomers, di-O-glucosides of heterodianthrone sennidins C and D.
Sennoside A and B both hydrolyze to give two molecules of glucose and the aglycones sennidin A and B. Sennidin A is dextrorotatory and B is its mesoform formed by intramolecular compensation.
Leave a Reply