Source
It is the piperidine alkaloid chiefly responsible for the pungency of the fruits of white and black pepper, Piper officinarum and Piper nigrum, Piperaceae. Isolated by H.C. Oersted in 1819, it is also found in long pepper (Piper longum – 1% to 2%) and West African pepper (Piper guineense). At least 5 alkaloids structurally related to piperine have been identified in pepper.
Uses
Pepper has been used since ages as a spice and was a much-prized spice of ancient Indian trade. One of the oldest and important spices, it is used as a stimulant digestive in indigenous medicine. Pepper was a much-valued spice used for various medicinal uses in several European countries into which it was exported from India through trade channels.
Piperine itself is added to food products to enhance aroma and flavour. It is also used as a biological insecticide.
Piperine is a much-researched alkaloid known for its anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, anti-carcinogenic, insecticidal and cytotoxic properties. By inhibiting enzymes crucial for drug and xenobiotic metabolism, piperine enhances the bioavailability of several drugs thus altering their effectiveness.
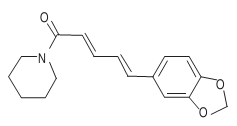
Description
When isolated, piperine is a pale yellow to yellow crystalline powder with a pungent odour and a burning after taste. Pungency of piperine is estimated at 100,000–200,000 Scoville units. It is slightly irritating to skin and eyes. Piperine is structurally related to capsaicin, the pungent principal of capsicum.
Piperine has molecular formula C17H19NO3 and the IUPAC name is 1-[5-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-oxo-2,4-pentadienyl] piperidine. It is slightly soluble in water (40 mg/L), soluble in alcohol, chloroform, ether and benzene. Piperine has a melting point of 131–135°C.
Leave a Reply