Digoxin is a purified cardioactive glycoside isolated from the dried leaves of Digitalis lanata or Digitalis orientalis (Scrophulariaceae). It is a secondary glycoside formed during drying, due to partial hydrolysis of the primary glycosides found in the fresh leaves. Several structurally related cardioactive glycosides are found in D. lanata and D. purpurea, two important sources of these therapeutically important glycosides. The primary glyscosides of D. purpurea are called Purpurea glycosides and those of D. lanata are lanatosides. While the former are based on three different aglycones with 3 molecules of digitoxose linked to the aglycone, those of lanatosides are based on 5 different aglycones and the digotixose farthest from the aglycone is acetylated. These C23 steroidal glycosides exert on the failing heart a slowing and strengthening effect due to which they are used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
While D. purpurea is of historical importance for use in the treatment of dropsy, digitoxin, digoxin, lanatoside C and desacetyl lanatoside C (deslanide) are the isolated digitalis constituents currently employed in therapy.
Acting similar to digitalis leaf, digoxin, first isolated by Sydney Smith in 1930, however has a rapid action. It is more rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is more quickly eliminated than digitoxin and is therefore more widely used of the cardioactive glycosides. It is also more hydrophilic than digitoxin and binds less strongly to plasma proteins and is mainly eliminated by the kidneys, whereas digitoxin is metabolized more slowly by the liver.
Uses
Over the past decades, digoxin has become the most widely used drug in the treatment of congestive heart failure. Proprietary preparations of lanatoside A and C are available in various countries but digoxin is more widely used. It is used for rapid digitalization to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure. Therapy with digoxin requires careful monitoring as its therapeutic index is very low. Digoxin preparations are commonly marketed under the name of Lanoxin, Digitek, Lanoxicap etc.
Description
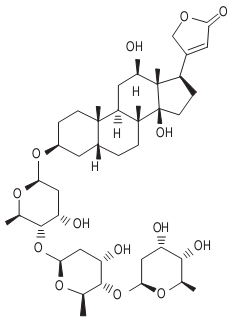
Digoxin, C41H64O14 – (3β-5β-12β) – [(O-2,6-Dideoxy-β-D-ribohexopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-o-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxyl]-12,14–dihydroxycard-20(22)-enolide, is constituted of aglycone digoxigenin attached to 3 molecules of digitoxose at the C-3 position. It is a white crystalline odourless powder with a bitter taste. Soluble in dilute (80%) alcohol, pyridine or mixture of chloroform and alcohol, it is almost insoluble in ether, acetone, ethyl acetate, chloroform and water (64.8 mg/L). It is very slightly soluble in 40% propylene glycol. Digoxin has a melting point of 248°C and forms radially arranged 4–5-sided triclinic plates from dilute alcohol or dilute pyridine. Its UVmax (ethanol) is 220 nm. Acid hydrolysis of digoxin yields 1 molecule of digoxigenin and 3 molecules of digitoxose.
Leave a Reply