Source
This alkaloid belongs to a group of modified benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids. A quarternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of isoquinoline alkaloids, it is found in many members of the Berberidaceae (Berberis and Mahonia species), Ranunculaceae (Hydrastis and Coptis species) and other families such as Anonaceae, Menispermaceae, Papaveraceae and Rutaceae. Berberine is found in the bark of the root, stem and branches either as the principal alkaloid or in association with other alkaloids such as hydrastine, canadine, berbamine, oxyacanthine, umbellatine, neprotine, nandinine, domesticine and thalletrine.
Uses
Plants containing berberine have long been used in traditional Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine. Berberis aristata called ‘Daruharidra’ is a reputed Ayurvedic drug used as a bitter tonic, stomachic, laxative, anti-pyretic and antiseptic. It is indicated for use in menorrhagia and neuralgia. Berberine has historical usage as a dye for its yellow colour. It is reported to have anti-amoebic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Today it is used in clinical practice for bacterial intestinal infections, trachomas and intestinal parasitic infections.
Description
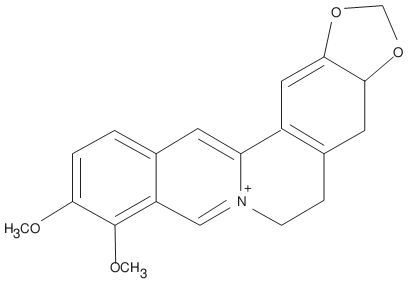
Coloured alkaloid berberine of molecular formula [C20H18NO4]+ is 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxy benzo(g)-1,3-benzodioxolo(5,6-a) quinolizinium. It occurs as a yellow-coloured, bitter-tasting powder soluble in water (1 in 4.5) or ethanol (1 in 100). It is easily soluble in hot water or hot ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene or chloroform, insoluble in ether or light petroleum. Aqueous solution is bitter to taste, alkaline in reaction and optically inactive. Berberine forms well-defined crystalline salts with acids and behaves as a quarternary base forming salts by replacement of the OH group. It forms yellow needles from ether with a melting point of 145°C. From water or dilute ethanol it crystallizes as bright yellow needles which on heating lose the water of hydration and on further heating decompose at 100°C. The hydrochloride salt crystallizes out in small needles when HCl is added to a warm aqueous solution of the alkaloid. It is soluble in about 500 parts of water but is almost insoluble in ethanol or dilute HCl.
Leave a Reply