It can be defined as the unit SDF in which the drug is enclosed in a soft shell made up of gelatin. The drug enclosed is usually in the form of solid, liquid or semi-solid.
It is a unit SDF available in various sizes and shapes such as spherical, tubular, oblongated, and ovoid.
Advantages
- It is suitable for solids, liquids, suspension, emulsions, volatile oils, semi-solids, etc.
- Disintegration is faster compared to hard gelatin capsules and tablets.
- Available in various sizes and shapes.
- It can be easily swallowed when compared to hard gelatin capsules.
- It cannot be used for drugs that are hygroscopic, effervescent and deliquescent in nature.
- It is not suitable for acidic drugs, ketones and aqueous products.
- The drugs that irritate the stomach extremely cannot be given in this dosage form.
Formulation of the capsule shell: The capsule shell is composed of gelatin material, water with higher concentration of plasticizer. It also contains additional ingredients such as preservatives, coloring agents, opacifying agents, flavoring agents, etc.
Some of the specifications during the manufacturing process are as follows:
- Gel strength or bloom strength: It is measured by using bloom gelometer, which determines the weight in grams required to depress a standard plunger from a fixed dispenser into the surface of a
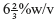 of gelatin solution under standard conditions. It measures the cohesive strength of the cross link between gelatin molecules, and it is directly proportional to the molecular weight of the gelatin. The standard range for bloom strength is between 150 and 250 bloom grams.
of gelatin solution under standard conditions. It measures the cohesive strength of the cross link between gelatin molecules, and it is directly proportional to the molecular weight of the gelatin. The standard range for bloom strength is between 150 and 250 bloom grams. - Viscosity: 25–45 mps (millipoise).
- Iron content: The iron content of the gelatin used for the manufacture of the soft gelatin capsules should not be more than 15 ppm because of its effects on the color used in the preparation and also possible chemical reaction in the product.
- Plasticizer: Its concentration to that of the gelatin should be in the range of 0.8:1, which renders the shells of elasticity and increases its plasticity. For example, glycerin, sorbitol, or combination.
Formulation of the blend: During the formulation of the blend when a product is determined to be dispensed in the liquid form, then the following two parameters are to be monitored:
- Base absorption factor: Formulation of suspension for gelatin encapsulation, the factor base absorption factor is considered. It can be defined as the number of grams of the liquid base required to produce an encapsulated mixture when mixed with 1 g of the solid drug.This can be determined by the following formula: Base absorption factor = Weight of the base/Weight of the solid
- Minim per gram factor: It can be defined as the volume in minims occupied by 1 g of the solid drug along with the weight of the liquid base required to form an encapsulated mixture. M/g = (BA + S)V/WM/g = Minim per gram factorBA = Weight of the baseS = 1 g of the solidV = Volume occupied by encapsulated mixtureW = Weight of the encapsulated mixture1 minim = 0.06 ml
Thus, lower the base absorption of the solids, higher will be the density of the mixture and hence smaller will be the size of the capsule shell.
Preservatives: These substances are included to prevent the microbial contamination of the shells as gelatin are obtained from animal source. Usually a combination of methyl paraben and propyl paraben are used.
Coloring agents: FD&C approved color dyes, pigments and lakes are used.
Opacifying agents: Titanium dioxide, aluminum hydroxide, etc.
Drugs: The drug, which is used for the soft gelatin capsules, may be in the form of the solid, liquid, or semi-solid. The volume of the capsule fill may range from 0.3 to 30 ml.
Manufacture of soft gelatin capsules: The manufacture of soft gelatin capsules is done by using rotary die process by form fill and seal (FFS) technique. In this method, the gelatin mass is fed by gravity on to an air cooled rotating drums. Gelatin films of controlled thickness are produced, which may vary from 0.022 to 0.045 inches and the gelatin film passes through the guider and comes in contact with two identical die-rollers, which rotate in opposite direction maintained at controlled temperature so that the gelatin film cavity is formed. The medicament to be capsulated flows by gravity into a positive displacement pump, which accurately dispenses the medicament into the gelatin wedge. After filling, by the movement of the rollers, the dies come in contact with each other such that the sealing of the capsules occur. The sealing of the capsules is achieved by mechanical pressure applied on the die rollers with the controlled temperature and relative humidity maintained. The sealed capsules are cut uniformly by the cutter and then immediately conveyed through naphtha belt to remove the excess of mineral oil lubricant. Finally, filled capsules are subjected to IR drying to remove the excess of moisture. Later the capsules are stored at specified temperature and humidity until packaged.
The soft gelatin capsules are usually blister or aluminum seal packed and the bulk package is carried out by using airtight plastic or glass container.
Differences between hard gelatin capsule and soft gelatin capsule are shown in Table 5.4.
Table 5.4 Differences between Hard Gelatin Capsule and Soft Gelatin Capsule
| Sl. No | Hard Gelatin Capsule | Soft Gelatin Capsule |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | They are made up of cap and body portions. | They are made as a single entity. |
| 2. | Only solid medicaments can be filled. | Solid, liquid, and semi-solid medicaments can be filled. |
| 3. | Disintegration time is low. | They undergo fast disintegration. |
| 4. | Capsule filled can be opened and sealed. | Once opened they cannot be sealed. |
| 5. | Capsule fill weight ranges between 100 and 950 mg. | Capsule fill volume ranges between 0.3 and 30 ml. |
| 6. | Available in only one shape. | Available in various shapes and sizes. |
| 7. | Concentration of plasticizer to gelatin ratio is low (0.4:1). | Concentration of plasticizer to gelatin ratio is more (0.8:1). |
Leave a Reply