Fairley and Kilgour, in 1966, grouped twenty amino acids into eight categories.
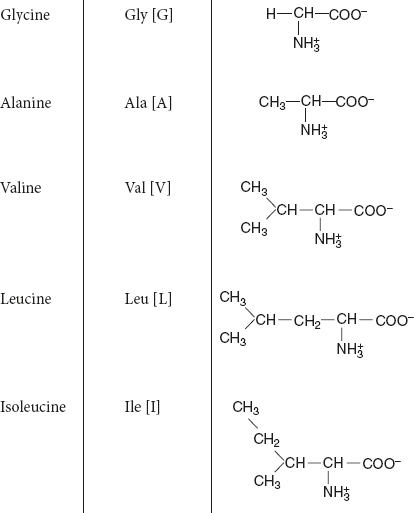
Simple amino acids: No functional group in their side chain.
Example: Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, and Ileu
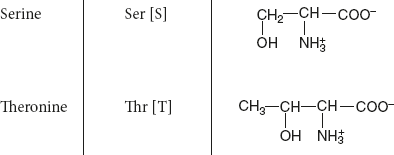
Hydroxy amino acids: Contain hydroxy group.
Example: Ser and Thre
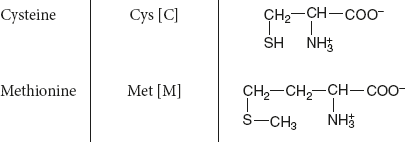
Sulphur amino acids: Contain sulphur group.
Example: Cys and Met
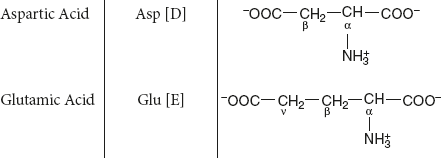
Acidic amino acids: Contain carboxyl group.
Example: Asp and Glu
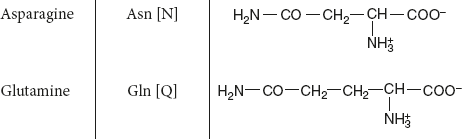
Amino acid amides: Derivatives of acidic amino acid whose one COO− group transformed into an amide group ![]() .
.
Example: Asn and Gln
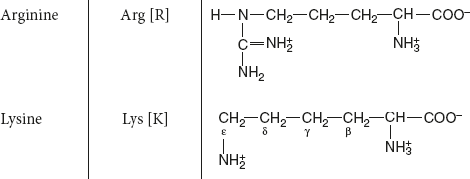
Basic amino acids: Contain amino group.
Example: Lys and Arg
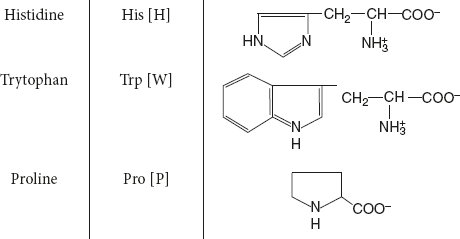
Heterocyclic amino acids: Have a side chain ring, which possesses one atom other than carbon.
Example: Trp, His, and Pro
Aromatic amino acids: Have benzene ring
Example: Phe and Tyr

Delimitations of this classification are as follows:
- Trp: This can also be included under aromatic.
- His: This can also be included under basic amino acids.
Leave a Reply