Learning Objective
- Tests used to determine the stability of suspensions
The following are the tests to determine the stability of suspensions:
- Determination of rate of sedimentation: Redispersibility is one of the major considerations in assessing the acceptability of the suspension. Since the sediment formed should be easily dispersed by moderate shaking, measurement of the sedimentation volume and its ease of redispersion form two of the most common evaluative procedures for suspensions.Measurement of sedimentation volume is carried out in a measuring cylinder under standard conditions.
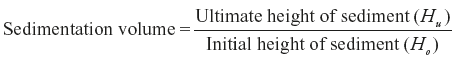 The larger this fraction, the better is the suspendability.Evaluation of redispersibility is carried out using a mechanical shaking device, which simulates the human arm motion during the shaking process.
The larger this fraction, the better is the suspendability.Evaluation of redispersibility is carried out using a mechanical shaking device, which simulates the human arm motion during the shaking process. - Determination of viscosity (Rheological method): The viscosity and the type of flow of the preparation are determined using a Brookefield’s viscometer at specified temperatures.
- Determination of zeta potential: Zeta potential controls flocculation of the dispersed phase. It can be determined by an instrument called Zetameter, which measures the electrophoretic mobility of particles in suspension.
- Determination of particle size change: There are chances that the particle size of the dispersed phase undergoes changes after storage of suspensions for a long time due to the effect of temperature on the suspensions. This results in the change in particle size distribution and crystal growth. This can be studied by Coulter counter or by microscopic method.
Leave a Reply