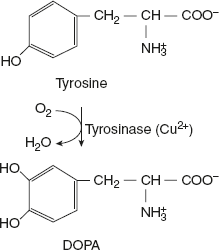
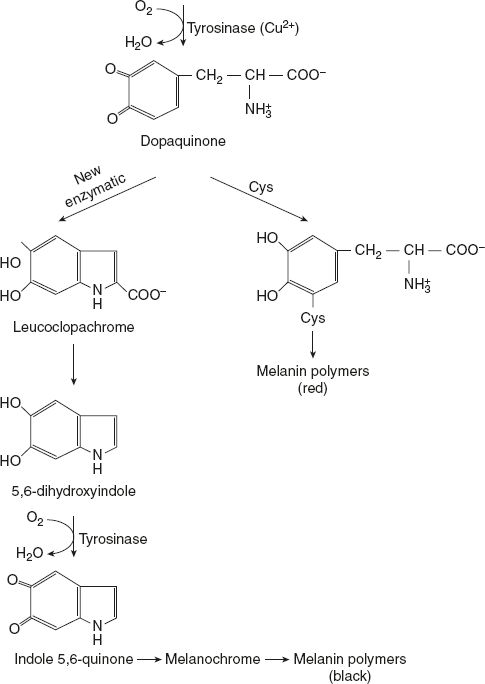
Melanin is the pigment of skin, hair, and eye. The synthesis of melanin occurs in melanosomes present in melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells. Tyrosine is the precursor for melanin and only one enzyme, namely tyrosinase, is involved in its formation. Tyrosinase hydroxylates tyrosine to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). DOPA can act as a cofactor for tyrosinase. The next reaction is also catalysed by tyrosinase, in which DOPA is converted to dopaquinone. It is believed that the subsequent couple of reactions occur spontaneously, forming leuco dopachrome followed by 5,6-dihydroxy indole. The oxidation of 5,6-dihydroxy indole to indole 5,6-quinone is catalysed by tyrosinase, and DOPA serves as a cofactor. This reaction, inhibited by tyrosine, regulates the synthesis of melanin. Melanochromes are formed from indole quinone, which, on polymerisation, is converted to black melanin.
Leave a Reply