- Reactions involving COOH group:Reaction with alkali (salt formation)The carboxylic group of amino acids releases H+ ion with the formation of carboxylate (COO−) ions. These may be neutralised by the cations like Na+ and Ca+ to form salts.
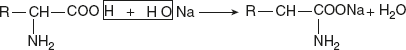 Sodium glutamate is used commercially as a flavouring agent.Reaction with alcohols (esterification)With alcohols, corresponding esters are produced.
Sodium glutamate is used commercially as a flavouring agent.Reaction with alcohols (esterification)With alcohols, corresponding esters are produced.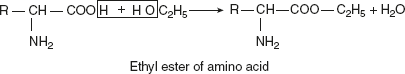 Significance: Isolation of amino acids in pure form from the protein hydrolysates.Reaction with aminesAmino acid reacts with amines and forms amides.
Significance: Isolation of amino acids in pure form from the protein hydrolysates.Reaction with aminesAmino acid reacts with amines and forms amides.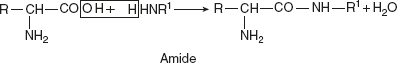
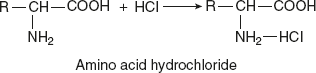
- Reactions involving NH2 group:Reaction with mineral acids (acid salt formation)When free amino acids are tested with protein and heated with mineral acids like HCl, acid salt is formed.
 Reaction with formaldehydeWith formaldehyde, the hydroxymethyl derivatives are formed. These derivatives are insoluble in water and resistant to attack by microorganisms.
Reaction with formaldehydeWith formaldehyde, the hydroxymethyl derivatives are formed. These derivatives are insoluble in water and resistant to attack by microorganisms.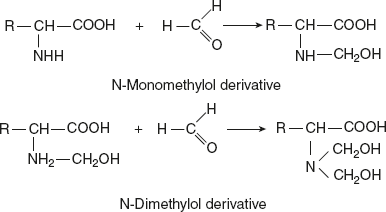 Significance: This reaction is the basis of the Sorensen titration method for determining the purity of individual amino acids.Reaction with nitrous acid (Van Slyke reaction)The amino acid reacts with HNO2 to liberate N2 gas and produce the corresponding α-hydroxy acids.
Significance: This reaction is the basis of the Sorensen titration method for determining the purity of individual amino acids.Reaction with nitrous acid (Van Slyke reaction)The amino acid reacts with HNO2 to liberate N2 gas and produce the corresponding α-hydroxy acids.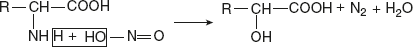 Reaction with acylating agents (acylation)Acylation is brought about by many acid chlorides and acid anhydrides, when an amino acid in alkaline medium reacts with CH3CoCl.
Reaction with acylating agents (acylation)Acylation is brought about by many acid chlorides and acid anhydrides, when an amino acid in alkaline medium reacts with CH3CoCl.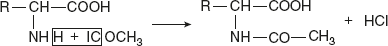 Reaction with FDNB or Sanger’s reagentIn mildly alkaline solution, FDNB (1 fluoro-2 4-dinitrobenzene) reacts with α-amino acids to produce yellow-coloured derivative, DNB-amino acid.
Reaction with FDNB or Sanger’s reagentIn mildly alkaline solution, FDNB (1 fluoro-2 4-dinitrobenzene) reacts with α-amino acids to produce yellow-coloured derivative, DNB-amino acid.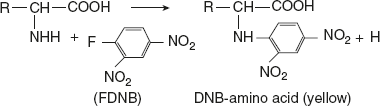 Significances: Valuable in elucidation of protein structure. Sanger successfully utilised this method in determining the sequence of amino acids in insulin.
Significances: Valuable in elucidation of protein structure. Sanger successfully utilised this method in determining the sequence of amino acids in insulin.
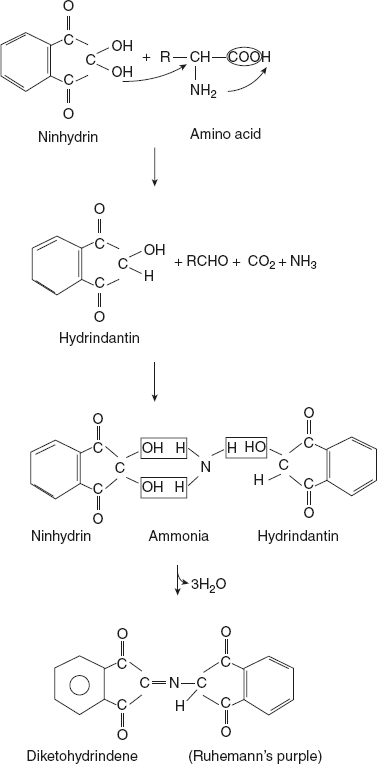
- Reaction involving both COOH and NH2 groups:Reaction with triketohydrindene hydrate (ninhydrin)Ninhydrin is reduced to hydrindantin when treated with amino acids. Amino acid is converted to ammonia, CO2, and aldehyde. The second molecule of ninhydrin reacts with the former hydrindantin and ammonia to form a purple-coloured complex.
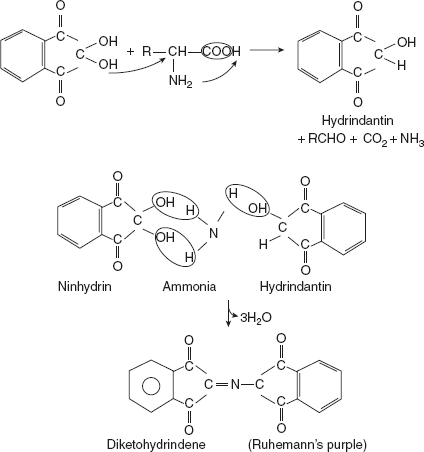 Reaction with phenyl isocyanateWith phenyl isocyanate, hydratonic acid is formed, which, in turn, can be converted to hydrindantin.
Reaction with phenyl isocyanateWith phenyl isocyanate, hydratonic acid is formed, which, in turn, can be converted to hydrindantin.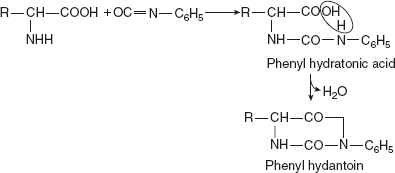 Reaction with phenyl isothiocyanate or Edman reagentPhenyl isothiocyanate also reacts similarly with amino acids to produce thiohydantoin acid. On treatment with acid in non-hydroxylic solvents, the latter cyclise to thiohydantoin.
Reaction with phenyl isothiocyanate or Edman reagentPhenyl isothiocyanate also reacts similarly with amino acids to produce thiohydantoin acid. On treatment with acid in non-hydroxylic solvents, the latter cyclise to thiohydantoin.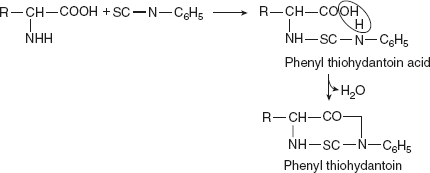 Significance: This reaction is useful in the study of protein structure.
Significance: This reaction is useful in the study of protein structure.
- Reaction involving the R or side chain groups or colour reaction:
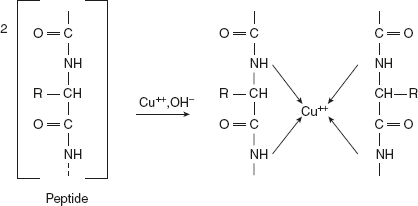
- Reaction involving the R or side chain groups or colour reaction:Biuret testThis test is a general test for compounds having a peptide bond. Alkaline copper sulphate reacts with compounds containing two or more peptide bonds to give a violet or pink-coloured product, which is due to the formation of coordination complex of cupric ion with unshared electron pairs of peptide nitrogen and oxygen of water.
 Xanthoproteic testAmino acid containing an aromatic nucleus (Tyr, Try, and Phe) forms yellow nitro derivative on heating with concentrated HNO3. The salts of these derivatives are orange in colour.
Xanthoproteic testAmino acid containing an aromatic nucleus (Tyr, Try, and Phe) forms yellow nitro derivative on heating with concentrated HNO3. The salts of these derivatives are orange in colour.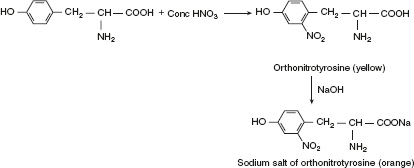 Millon’s testAmino acids or compounds containing hydroxy benzene radical react with Millon’s reagent (mercurous and mercuric nitrate containing HNO3) form a red complex. Thus, this test is specific for tyrosine.
Millon’s testAmino acids or compounds containing hydroxy benzene radical react with Millon’s reagent (mercurous and mercuric nitrate containing HNO3) form a red complex. Thus, this test is specific for tyrosine.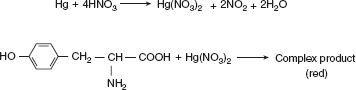 Hopkins-Cole testHopkins–Cole reaction is due to the presence of the indole ring of amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan in the presence of glyoxalic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid gives a purple colour.Glyoxalic acid can be prepared by reducing oxalic acid with magnesium powder or sodium amalgam or glacial acetic acid, which has been exposed to sunlight. It also contains glyoxylic acid.
Hopkins-Cole testHopkins–Cole reaction is due to the presence of the indole ring of amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan in the presence of glyoxalic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid gives a purple colour.Glyoxalic acid can be prepared by reducing oxalic acid with magnesium powder or sodium amalgam or glacial acetic acid, which has been exposed to sunlight. It also contains glyoxylic acid.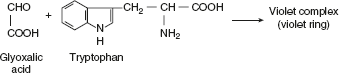 Pauly’s TestDiazotised sulphanilic acid couples with amines, phenols, and imidazole to form highly coloured compounds. The diazonium compound is only formed in the cold condition, and so all solutions must be cooled in ice before diazotisation.
Pauly’s TestDiazotised sulphanilic acid couples with amines, phenols, and imidazole to form highly coloured compounds. The diazonium compound is only formed in the cold condition, and so all solutions must be cooled in ice before diazotisation.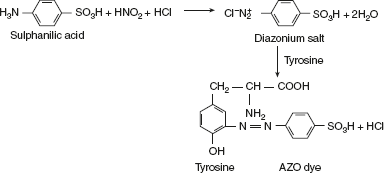 Sakaguchi reactionThis reaction is given by guanidium compounds. The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine.
Sakaguchi reactionThis reaction is given by guanidium compounds. The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine.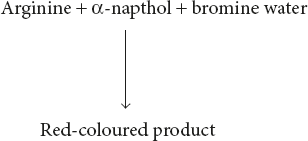 Sulphur test
Sulphur test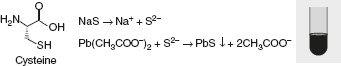 Sodium nitroprusside test
Sodium nitroprusside test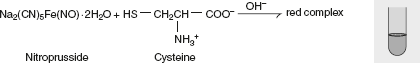
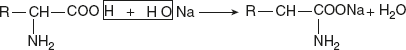 Sodium glutamate is used commercially as a flavouring agent.Reaction with alcohols (esterification)With alcohols, corresponding esters are produced.
Sodium glutamate is used commercially as a flavouring agent.Reaction with alcohols (esterification)With alcohols, corresponding esters are produced.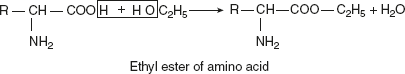 Significance: Isolation of amino acids in pure form from the protein hydrolysates.Reaction with aminesAmino acid reacts with amines and forms amides.
Significance: Isolation of amino acids in pure form from the protein hydrolysates.Reaction with aminesAmino acid reacts with amines and forms amides.
 Reaction with formaldehydeWith formaldehyde, the hydroxymethyl derivatives are formed. These derivatives are insoluble in water and resistant to attack by microorganisms.
Reaction with formaldehydeWith formaldehyde, the hydroxymethyl derivatives are formed. These derivatives are insoluble in water and resistant to attack by microorganisms. Significance: This reaction is the basis of the Sorensen titration method for determining the purity of individual amino acids.Reaction with nitrous acid (Van Slyke reaction)The amino acid reacts with HNO2 to liberate N2 gas and produce the corresponding α-hydroxy acids.
Significance: This reaction is the basis of the Sorensen titration method for determining the purity of individual amino acids.Reaction with nitrous acid (Van Slyke reaction)The amino acid reacts with HNO2 to liberate N2 gas and produce the corresponding α-hydroxy acids. Reaction with acylating agents (acylation)Acylation is brought about by many acid chlorides and acid anhydrides, when an amino acid in alkaline medium reacts with CH3CoCl.
Reaction with acylating agents (acylation)Acylation is brought about by many acid chlorides and acid anhydrides, when an amino acid in alkaline medium reacts with CH3CoCl. Reaction with FDNB or Sanger’s reagentIn mildly alkaline solution, FDNB (1 fluoro-2 4-dinitrobenzene) reacts with α-amino acids to produce yellow-coloured derivative, DNB-amino acid.
Reaction with FDNB or Sanger’s reagentIn mildly alkaline solution, FDNB (1 fluoro-2 4-dinitrobenzene) reacts with α-amino acids to produce yellow-coloured derivative, DNB-amino acid. Significances: Valuable in elucidation of protein structure. Sanger successfully utilised this method in determining the sequence of amino acids in insulin.
Significances: Valuable in elucidation of protein structure. Sanger successfully utilised this method in determining the sequence of amino acids in insulin. Reaction with phenyl isocyanateWith phenyl isocyanate, hydratonic acid is formed, which, in turn, can be converted to hydrindantin.
Reaction with phenyl isocyanateWith phenyl isocyanate, hydratonic acid is formed, which, in turn, can be converted to hydrindantin. Reaction with phenyl isothiocyanate or Edman reagentPhenyl isothiocyanate also reacts similarly with amino acids to produce thiohydantoin acid. On treatment with acid in non-hydroxylic solvents, the latter cyclise to thiohydantoin.
Reaction with phenyl isothiocyanate or Edman reagentPhenyl isothiocyanate also reacts similarly with amino acids to produce thiohydantoin acid. On treatment with acid in non-hydroxylic solvents, the latter cyclise to thiohydantoin. Significance: This reaction is useful in the study of protein structure.
Significance: This reaction is useful in the study of protein structure.
 Xanthoproteic testAmino acid containing an aromatic nucleus (Tyr, Try, and Phe) forms yellow nitro derivative on heating with concentrated HNO3. The salts of these derivatives are orange in colour.
Xanthoproteic testAmino acid containing an aromatic nucleus (Tyr, Try, and Phe) forms yellow nitro derivative on heating with concentrated HNO3. The salts of these derivatives are orange in colour. Millon’s testAmino acids or compounds containing hydroxy benzene radical react with Millon’s reagent (mercurous and mercuric nitrate containing HNO3) form a red complex. Thus, this test is specific for tyrosine.
Millon’s testAmino acids or compounds containing hydroxy benzene radical react with Millon’s reagent (mercurous and mercuric nitrate containing HNO3) form a red complex. Thus, this test is specific for tyrosine.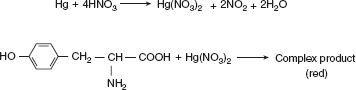 Hopkins-Cole testHopkins–Cole reaction is due to the presence of the indole ring of amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan in the presence of glyoxalic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid gives a purple colour.Glyoxalic acid can be prepared by reducing oxalic acid with magnesium powder or sodium amalgam or glacial acetic acid, which has been exposed to sunlight. It also contains glyoxylic acid.
Hopkins-Cole testHopkins–Cole reaction is due to the presence of the indole ring of amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan in the presence of glyoxalic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid gives a purple colour.Glyoxalic acid can be prepared by reducing oxalic acid with magnesium powder or sodium amalgam or glacial acetic acid, which has been exposed to sunlight. It also contains glyoxylic acid. Pauly’s TestDiazotised sulphanilic acid couples with amines, phenols, and imidazole to form highly coloured compounds. The diazonium compound is only formed in the cold condition, and so all solutions must be cooled in ice before diazotisation.
Pauly’s TestDiazotised sulphanilic acid couples with amines, phenols, and imidazole to form highly coloured compounds. The diazonium compound is only formed in the cold condition, and so all solutions must be cooled in ice before diazotisation. Sakaguchi reactionThis reaction is given by guanidium compounds. The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine.
Sakaguchi reactionThis reaction is given by guanidium compounds. The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine. Sulphur test
Sulphur test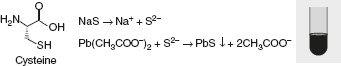 Sodium nitroprusside test
Sodium nitroprusside test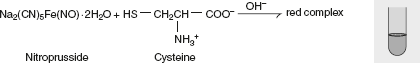
Leave a Reply