Inhibition can occur during two reactions in glycolysis.
Glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate + H3Po4 → 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid + NADH + H+
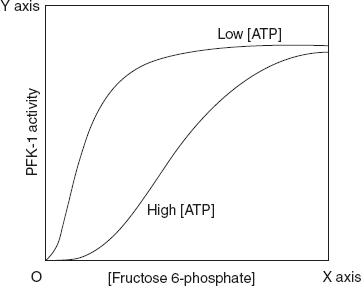
Figure 8.7 Graphical Representation of Allosteric Inhibition of Phosphofructokinase with Respect to ATP Concentration
This reaction may be inhibited by iodoacetate; arsenate can also interfere with this reaction, not by inhibition, but by competing with phosphate in the first carbon atom to form 1-areseno 3-phosphoglycerate, which hydrolyses spontaneously to give 3-phosphoglyceric acid without generating ATP in the next step. This is an example of uncoupling of oxidation from phosphorylation.
2-phosphoglyceric acid → Phosphoenol pyruvate + H2O
Enolase, which catalyses this reaction, is inhibited by fluoride. Addition of fluoride to blood prior to glucose estimation prevents glycolysis.
Leave a Reply