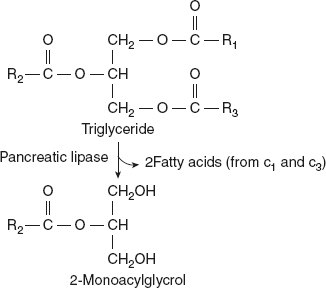
Triacylglycerols are too large to be taken by the mucosal cells of the intestinal villi. Hence, they are acted upon by an esterase, pancreatic lipase, which removes the fatty acids at carbon 1 and 3. The resulting products of hydrolysis are a mixture of 2-monoacylglycerol and free fatty acids. A second protein, colipase is secreted by the pancreas, which also helps to hold and stabilise the lipase at the lipid–aqueous interface.
Leave a Reply