Competitive inhibitors are used in clinical and biological situations. They are frequently called antagonists or antimetabolites of the substrates with which they compete.
- Treatment of Gout
- Xanthine oxidase is an enzyme of purine catabolism, which catalyses the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid.
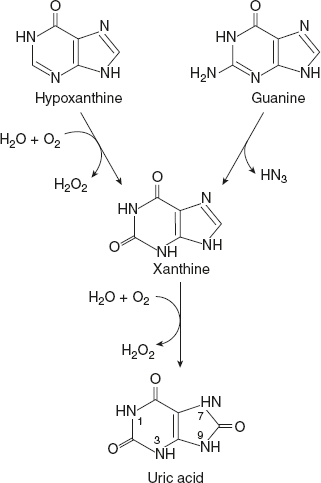
- Xanthine oxidase is a dimeric proteins of identical 130kD subunits, each of which contains a few election transfer agents – an FAD, an Mo complex that cycles between its Mo(VI) and Mo(IV) oxidation state and two different Fe-S clusters.
- Allopurinol, an analog of hypoxanthine, in which the position of N7 and C8 are interchanged competitively, inhibits xanthine oxidase.
- Xanthine oxidase is an enzyme of purine catabolism, which catalyses the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid.
Leave a Reply