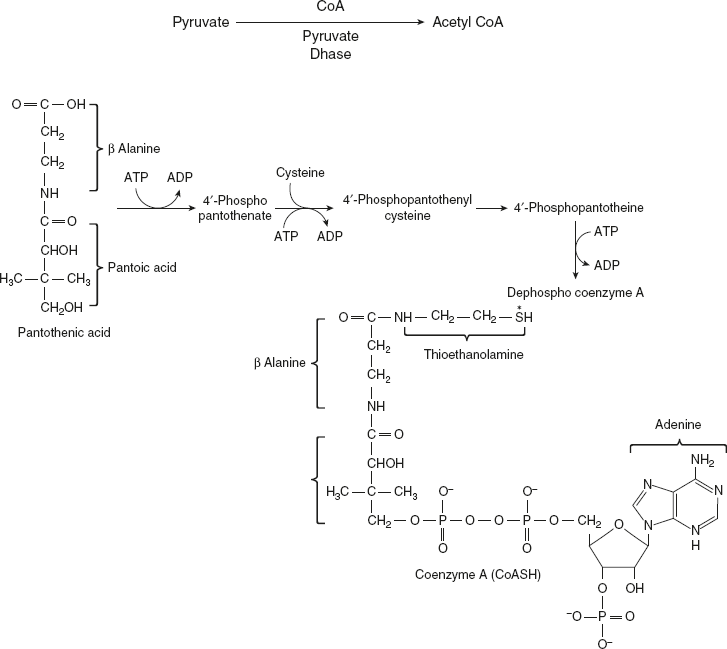
The functions of pantothenic acid are excreted through coenzyme A or CoA.
CoA is a central molecule involved in the entire metabolism (carbohydrate, lipid, and protein).
Coenzyme A has a terminal thiol or sulfhydryl group (SH), which is the reactive site; hence, CoA SH is also used. Acyl group (free fatty acid) is linked to coenzyme A by a thioester bond to give acyl CoA. When bound to acetyl unit, it is called acetyl CoA, and with succinate, succinyl CoA is formed.
Leave a Reply