Hyaluronic acid is made up of repeating units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine (Figure 2.19). When it is subjected to hydrolysis, it forms D-glucosamine, D-glucuronic acid, and acetic acid. It is also hydrolysed by the enzyme hyaluronidase present in spleen and testicular tissues. The main action of this enzyme is to reduce the viscosity of hyaluronic acid, which as a result rapidly spreads in the tissues. Hence, hyaluronidase is also known as a spreading agent.
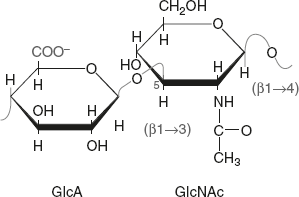
Figure 2.19 Structure of Hyaluronic Acid
Leave a Reply