This is also called cytochrome bc1 complex or ubiquinone, cytochrome-oxidoreductase. This couples the transfer of electrons from ubiquinol (QH2) to cytochrome c with the vectorial transport of protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
Net equation for the redox reactions of Q cycle:
QH2 + 2Cyt c1 (oxidised) + 2H + N → Q + 2Cyt c1 (reduced) + 4H + p
The Q cycle accommodates the switch between the two electron-carrier ubiquinones and the one electron-carrier’s cytochrome b562, b566, c1, c.
Complex III contains cyt b562, cyt b566, cyt c1, and cyt c iron-sulphur protein and at least six other proteins subunits. These proteins are asymmetrically disposed in the inner mitochondrial membrane; cyt b spans the membrane.
Complex III functions as a proton pump, as a result of the asymmetric orientation of the complex. The protons produced when UQH2 is oxidised to UQ are released to the intermembrane space, producing a transmembrane difference of proton concentration, a proton gradient is formed refer Figure 8.18. The importance of this proton gradient to mitochondrial ATP synthesis will soon become clear.
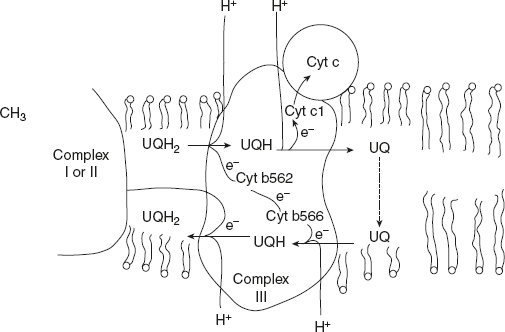
Figure 8.18 Flow of Electrons through Complex III
Leave a Reply