The synthesis of purine and pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides occurs from ribonucleotides by a reduction of the C2 of ribose moiety as shown in Figure 11.5. This reaction is catalysed by a multi-subunit (two B1 and two B2 subunits) enzyme ribonucleotide reductase.
The ribonucleotide reductase itself provides the hydrogen atoms needed for the reduction from its sulfhydryl groups. The reducing equivalents, in turn, are supplied by thioredoxin, a monomeric proteins with two cysteine residues. NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase converts the oxidised thioredoxin to reduced form, which can be recycled again and again. Thioredoxin thus serves as a cofactor in an enzymatic reaction.
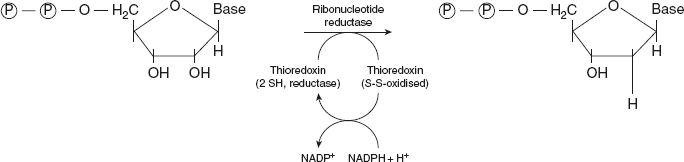
Figure 11.5 Conversion of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides
Leave a Reply