Source
Eugenol is a phenyl propene extracted from the essential oil of clove, Eugenia caryophyllus (Myrtaceae). Though clove is the richest source, it is also found in nutmeg, cinnamon, basil, turmeric, marjoram, bay leaf and many other culinary and medicinal plants. It is the chief aroma chemical of essential oil of clove in which it is present up to 75% to 90%. Other significant sources from which it may be isolated are pimento –80%, cinnamon leaf oil –95% and bay leaf oil –50%. Eugenol is also found in varying amounts in a number of flowers such as rose, acacia, neroli etc.
Uses
A phenyl propanoid, its name is derived from its source Eugenia. Eugenol and the essential oil of clove are used in perfumery and flavouring and as an antiseptic and anaesthetic medicinally. Its pleasant, spicy pungent odour makes it valuable in perfumery and flavouring. Cloves have been used since long as a spice and a food preservative. As a complex with zinc oxide, it is used as a prosthodontic in dentistry. Eugenol derivatives are used in perfumery, flavouring and as stabilizers and antioxidants for plastics and rubber. Its antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties are well reported. Earlier it was used for the production of isoeugenol for the manufacture of vanillin.
Description
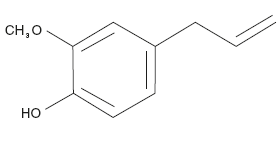
Eugenol or 4-allyl-2-methoxy phenol is an aromatic liquid of molecular formula C10H12O2. Its IUPAC name is 2-Methoxy -4(Prop -2 –en-1-yl) phenol. It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with a strong odour of cloves. It has a boiling point of 256°C and specific gravity of 1.064–1.07. It has a refractive index of 1.54–1.542. Eugenol is stable, combustible and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. It is slightly soluble in water and fully miscible with organic solvents such as cyclohexane, ethanol, dichloromethane, toluene, benzene, propylene glycol and diethyl ether.
Leave a Reply