Learning Objective
- Tablet excipients and their properties
Compressed tablets usually contain active medicament/s mixed with a number of inert substances known as excipients or additives. These additives are added to give good quality tablets. Although these additives are termed inert, they have great influence on stability, bioavailability and process by which dosage forms are prepared.
According to the activity of the additives in the preparation of tablet they may be classified as follows:
- Diluents: When the dose of drug is very small, it is not practicable to compress such small amount in the form of a tablet, and then the inert substances are added to increase the bulk of the powders to be easily compressible into the tablets.Example: Lactose, starch, mannitol, calcium carbonate and dicalcium phosphate.
- Binders: The agents used to impart cohesiveness or glue to powdered substances are known as binders. They keep tablet intact after compression. The type of binder depends upon binding force required to form granules and its compatibility with other compounds. The optimum concentration of the binder addition into the tablet formulation is very critical as it is one of the rate limiting steps for the disintegration, onset of action and bioavailability (Table 5.1). Table 5.1 List of Binders, Their Solvents and Their Optimum ConcentrationBinderSolventConcentrationAcaciaWater/water-alcohol mixture2–5%TragacanthWater1–3%GelatinWater1–4%SucroseWater2–20%StarchWater1–4%Sodium carboxymethyl celluloseWater1–4%Ethyl celluloseWater/water-alcohol mixture0.5–2%Polyvinyl
pyrrolidoneWater/water-alcohol mixture2–6% - Disintegrating agents/Disintegrants: These are the substances added to facilitate the disintegration or breaking apart of the tablet into small particles in GIT after administration and facilitating dissolution. Usually disintegrants are added in two steps:
- Intragranular disintegrants: Disintegrants are added during granulation process and it enhances the disintegration of the granules.
- Intergranular disintegrants: Disintegrants are added during the blending or lubrication stage before the compression process to facilitate bursting of the tablet into granules, when it comes in contact with the liquid.
- Substances that swell up when they come in contact with moisture or solvent.
- Substances that react with effervescence when they come in contact with moisture.Example: Maize starch, potato starch, Veegum, methyl cellulose, agar, bentonite, CMC, and sodium starch glycolate, citric acid, tartaric acid with sodium bicarbonate.
- Lubricants: These are the substances, which are added to granules during blending process to facilitate the easy ejection of tablet from the die cavity after compression.Example: Magnesium stearate, Calcium stearate, Talc, etc.
- Glidants: These are the substances, which are added during blending process before compression of tablet for easy flow of granules from hopper into die cavity. They act by reducing the inter particle friction between granules such that flow property is increased.Example: Silicates and colloidal silica.
- Anti-adherents: These are the substances used to prevent sticking of tablet surface material to the punches and the tablet die wall. It avoids processing problems of sticking and picking, which occur due to the presence of excess of moisture.Example: Talc and corn starch. Some more examples are provided in the table below.
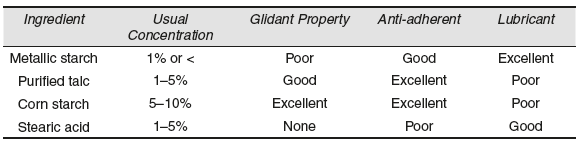
- Coloring agents: They are used to impart elegance to the tablets. They are also used to identify the different types of tablets. Only FD&C approved color dyes are used. The colorants should be physically and chemically stable with other excipients, effective in low concentration, pharmacologically inert and should not interfere with the assay procedure of the medicament.Example: Frequently used colorants and their common names are mentioned in the table below.ColorantsCommon NameFDC Blue #1Brilliant blueFDC Blue #2Indigo tineFDC Red #3ErythromycinFDC Yellow #5TartrazineFDC Yellow #6Sunset yellow
- Flavoring agents: These are the substances usually used to increase the palatability of oral cavity tablets. The choice of the flavoring agent depends on the patient age and type of preparation also.Example: Peppermint oil, mango flavor, fruit flavor, chocolate flavor and vanilla flavor.
- Sweetening agents: They are added to tablets, which are required to be dissolved in buccal cavity and to mask the unpleasant or bitter taste of the drug. The bases for the formulation are already sweet and they impart sweetness of varying degree.Example: Lactose, sucrose, saccharin, and cyclamates.
Leave a Reply