The inhibitors involved in the electron transport arrest respiration by combing with membranes of the respiratory chain rather than with the enzymes that are involved in coupling respiration with ATP synthesis. They appear to act at three loci that may be identical to the energy transfer sites I, II, and III as stated in the below Figure.
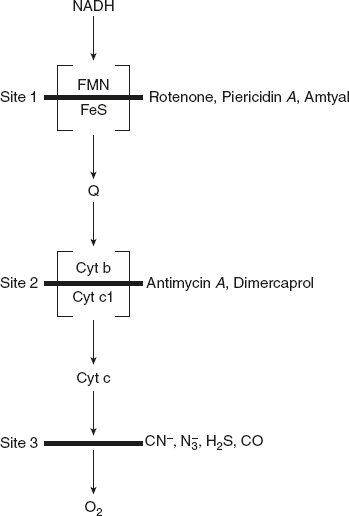
Site of Action of Inhibitors in ETC Chain
- Rotenone:Rotenone is a compound extracted from the roots of tropical plant. It complexes avidly with NADH dehydrogenase and acts between Fe-S proteins and ubiquinone. Rotenone is relatively non-toxic to mammals because it is absorbed poorly although exposure of the lungs to dust is a little more dangerous.
- Piericidin A:It is an antibiotic produced by streptomyces. It has an action similar to that of rotenone.
- Barbiturates:Barbiturates block NADH dehydrogenase but it is required in much higher concentration for the purpose of sedative action on neural membranes and also for inhibition of respiration.
- Amytal:Does not interfere with the oxidation of succinate because the electrons of these substrates enter the electron transport chain beyond the block of coenzyme Q.
- Antimycin:It’s an antibiotic produced by streptomyces. It inhibits the respiratory chain at or around site II and blocks electron flow between cytochromes b and c1, which prevent ATP synthesis coupled to the generation of a proton gradient at site II. This block can be bypassed by the addition of ascorbate, which directly reduces cytochromes.
- Dimercaprol:It is an identical action to the antimycin.
- Cyanides:These are among the poisons better known by public. They enter the tissues very rapidly so that a sufficient quantity becomes lethal within a few minutes. The cyanide ion (CN−) combines tightly with cytochrome oxidase
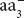 , leading to the cessation of transfer of electrons to oxygen. The previous electron carriers in the chain accumulate in their reduced state, and generation of high energy phosphate stops.
, leading to the cessation of transfer of electrons to oxygen. The previous electron carriers in the chain accumulate in their reduced state, and generation of high energy phosphate stops. - Azide:It also blocks the electron flow between the cytochrome oxidase complex and O2. Azide
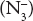 , also cyanide, reacts with the ferric form (Fe3+) of this carrier.
, also cyanide, reacts with the ferric form (Fe3+) of this carrier. - Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S):Its action is similar to HCN.
- Carbon Monoxide:It also attacks between cytochrome oxidase and O2 while cyanide and azide CO inhibit the ferrous form (Fe2+) of the electron carrier.
Leave a Reply