E + S → ES → E + P
++
I I
I I
I I
EI ESI
KI = [E][I]/[EI]

Ki = [ES]/[ESI]



ET = E + ES + ESI + EI
= [E] + [ES] + [ES][I]/KI + [E][I]/KI
= [E] (1 + I/Ki) + [ES](1 + I/Ki)
= Km [ES]/[S] + [ES](1 + I/KI)
= [ES](Km/[S] + 1) (1 + I/KI)
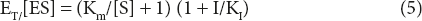
For enzyme-catalysed reaction:



Substituting (8) in (5), we get
Vmax /V = (Km/[S] +)(1 + I/KI)
Vmax /V = (Km + [S]/[S])(1 + I/KI)
V/Vmax = [S]/Km + [S]) × 1/1 + I/KI)
V = Vmax[S]/(Km + [S]) × 1/1 + I/KI)
Dividing by (1 + I/KI) in numerator and denominator,
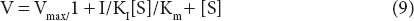

Where
Vmaxapp = Vmax/1 + I/Ki
This is the M–M equation for non-competitive inhibitor refer Table 6.9.
From equation (10), it is clear that when an enzyme is inhibited non-competitive, Vmax decreases and Km value does not change; that is, the combination with either [S] or [I] does not affect the affinity for the other as shown in Figure 6.22.
Table 6.9 M–M equation (Slope, X-intercept, Y-intercept)
| Slope(M) | Km(1 + I/KI)/Vmax |
| Y intercept | 1 + I/KI/Vmax |
| X intercept | −1/Km |
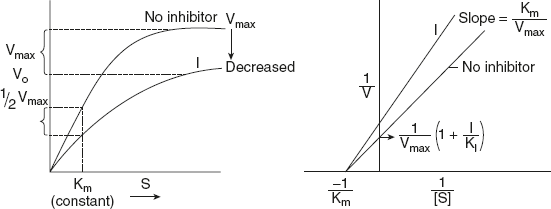
Figure 6.22 Effect of Non-competitive Inhibitor
Leave a Reply