Skin can act as a barrier and prevent deep penetration of drug molecules. Percutaneous absorption of most drugs is a passive diffusion process that can be described by Fick’s first law of diffusion. In the initial diffusion stage, drug molecules may penetrate the skin along the hair follicles or sweat ducts and then be absorbed through the hair follicular epithelium and sebaceous glands. When a steady state has been reached, diffusion through stratum corneum becomes the dominant pathway.
The membrane-limited flux under steady condition is described by the expression
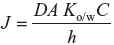
where
J = Amount of drug passing through the membrane per unit area, unit time
D = Diffusion coefficient of the skin
A = Area of the membrane
Ko/w = Membrane or vehicle partition coefficient
C = Drug concentration in the vehicle or delivery system
h = Thickness of the membrane
Leave a Reply