All amino transferase requires the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (a derivative of vitamin B6), which is covalently linked to an e-amino group of a specific lysine residue at the active site of the enzyme (Schiff base) as shown in Figure 9.4.
Amino transferase transfers the amino group from an amino acid to the pyridoxal part of the coenzyme to produce pyridoxamine phosphate. The pyridoxamine form of coenzyme then reacts with an α-keto acid to form an amino acid and returns to its original form of coenzyme.
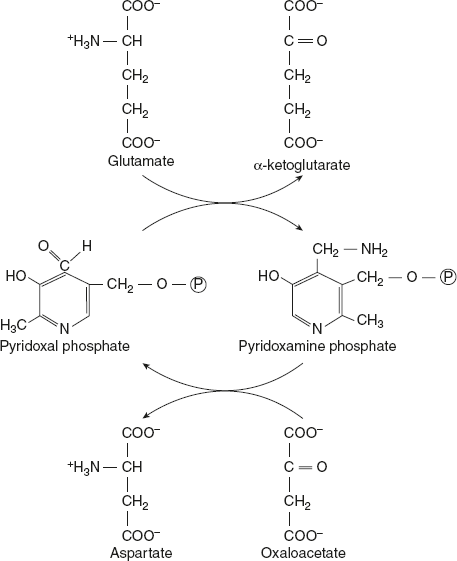
Figure 9.4 Mechanism of Transamination
Leave a Reply