Friability test Friability in addition to hardness gives the measure of tablet strength. It is defined as its resistance to shock and abrasion encountered during the process of manufacture, packing, transport and ultimately its usage.
Factors contributing to tablet friability are deep concave punches used during the compression leading to formation of whiskered tablets, high moisture content of the granules, over drying of the granules, etc. It is determined using the instrument Roche friabilator, and the value is calculated using the following equation:
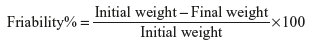
The batch tablets pass the test for friability, if the value is less than 1%.
Weight variation test: The average weight is determined by randomly selecting 20 tablets and weighing them individually. Not more than two of the individual weights deviate from the average weight by more than the percentage given in the pharmacopeia and none deviates by more than twice that percentage. IP limits for tablet weight variation are given as follows:
| IP/BP | Limit |
|---|---|
| 80 mg or less | 10% |
| More than 80 mg and less than 250 mg | 7.5% |
| 250 mg or more | 5% |
Drug content: Thirty tablets are selected randomly. Ten of these tablets are assayed individually. The tablet passes the test if 9 of the 10 tablets contain not less than 85% and not more than 115% of the labeled drug content (±15%) and the 10th tablet may not contain less than 75% and more than 125% of the labeled content (±25%). If these conditions are not met, then the remaining 20 tablets are assayed individually. The batch sample complies with the test if the drug content of not more than 3 individual tablets out of the total 30 sampled tablets is outside the limits by ±15% and none may fall outside of the limits of ±25%.
Disintegration test: This method is used to evaluate the rate of disintegration of SDF of tablets. Disintegration is defined as the breakdown of SDF into small particles after it is ingested. The time of disintegration is a measure of the quality. If the disintegration time is too high, it suggests that the tablet is highly compressed. Also, if the disintegration time is not uniform in a set of samples being analyzed, it indicates batch inconsistency and lack of batch uniformity. The test is performed by randomly selecting six tablets using the instrument Disintegration Test Apparatus.
Some of the types of dosage forms and their disintegration tests are as follows:
- Uncoated tablets: Tested using distilled water as medium at 37 ± 2 °C at 29–32 cycles per minute. The test is completed if all the tablets disintegrate within 15 minutes. It is acceptable when there is no palpable core at the end of the cycle and if the mass does not stick to the immersion disc.
- Coated tablets: The test procedure given for uncoated tablets is adopted. For film coated tablets, the disintegration time limit is 30 minutes and for sugar coated tablets it is 60 minutes.
- Enteric coated/Gastric resistant tablets: The test is carried out first in 0.1M HCl (up to 2 hours during which all the tablets should be completely intact followed by replacement with phosphate buffer pH 6.8 for 1 hour during which the tablets should disintegrate.
Dissolution test: Dissolution is pharmaceutically defined as the rate of mass transfer from a solid surface into the dissolution medium or solvent under standardized conditions of liquid or solid interface, temperature and solvent composition. It is a dynamic property that changes with time and explains the process by which a homogenous mixture of a solid or a liquid can be obtained in a solvent.
Dissolution test can be performed in two ways—in vitro, in vivo.
In vivo test is performed in selected animal and human subjects (expensive and time consuming).
In vitro test is performed using dissolution test apparatus (inexpensive and less time consuming).
Factors to be considered for designing in vitro dissolution test are as follows:
- Factors related to the dissolution apparatus
- Factors related to dissolution fluid or medium
- Factors related to the test medium
Dissolution test apparatus-1 (basket type): The sample which floats in the test media is placed in a small wire mesh basket attached to the bottom of the shaft connected to a variable speed motor. The basket is immersed in a dissolution medium (as specified in monograph) contained in a 1000 ml flask. The flask is cylindrical with a hemispherical bottom. The flask is maintained at 37±0.5 °C by a constant temperature bath. The motor is adjusted to turn at the specified speed and samples of the fluid are withdrawn at predetermined time intervals to determine the amount of drug in solutions.
Dissolution test apparatus-2 (paddle type): It is same as apparatus-1, except the basket is replaced by a paddle. The dosage form is allowed to sink to the bottom of the flask before stirring. For dissolution test USP specifies the dissolution test medium and volume, type of apparatus to be used, rpm of the shaft, time limit of the test, and assay procedure for the same. The test tolerance is expressed as a percentage of the labeled amount of drug dissolved in the time limit.
Leave a Reply