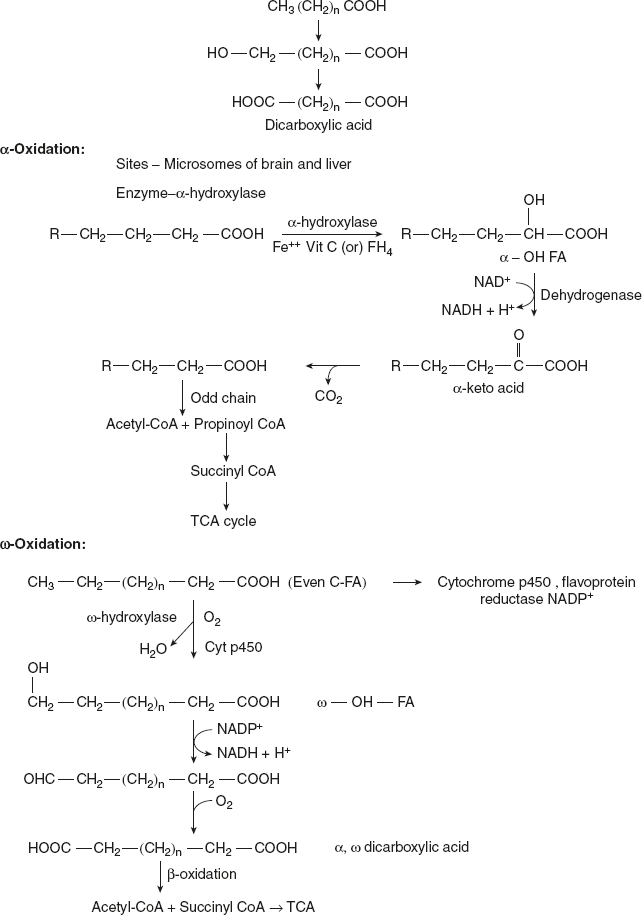
β-oxidation is the most predominant pathway for fatty acid degradation. However, the removal of one carbon unit at a time by oxidation of α-carbon atom of fatty acid is known as α-oxidation.
This type of oxidation has been detected in brain tissues. It does not require CoA intermediates and does not require high energy phosphates.
ω-oxidation is a minor pathway and is brought about by hydrolase enzymes involvng cytochrome p450 in the endoplasmic reticulum. The CH3 group is converted to CH2OH group that is subsequently oxidised to COOH, thus forming dicarboxylic acid. This is β-oxidised usually to adipic and suberic acids which are excreted in urine.
Leave a Reply