Addition reaction
Isomerism: Unsaturated fatty acids may have isomers, depending upon two factors. One type of isomerism depends upon the position of double bond in the hydrocarbon chain – positional isomerism.
Example: Oleic acid. There are sixteen positions where the double bonds may be placed. Hence, oleic acid forms sixteen isomers.
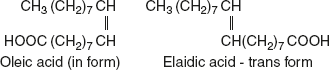
Geometrical isomerism: It depends on the oxidation of the radicals around the axis of double bond. If the radicals are on the same side of the double bond, the compound is a cis form of isomer. If they are on opposite side of the double bond, it is a trans form of isomer.
Leave a Reply