The dosing, performance and the clinical efficacy of aerosol products especially a MDI is dependent on the design of the container and valve. The efficiency and performance of the valve is determined by the following tests.
Valve discharge rate gives the amount of contents dispensed in grams per second. The aerosol can is weighed and the contents are dispensed for a fixed time using a standard apparatus. The container is reweighed and the difference in weight divided by the time gives the valve discharge rate.
Dose uniformity test is carried out to determine whether the patient receives the same dose of the medicament, every time the value is depressed. The test can be done in two ways.
- Dispensing one or two doses into a solvent or onto a material that absorbs the active ingredient, and then assaying the amount of active ingredient in the solvent or sample.
- Weighing a filled container, dispensing several doses of the product and reweighing the container. The difference in weight, divided by the number of doses dispensed, gives the average dose.
The spray pattern of different products and different valves is carried out as follows. The product is sprayed on a piece of filter paper that has been treated with a dye-talc mixture. Based on the nature of the aerosol, oil soluble or water soluble dye is used. The particles that strike the paper cause the dye to go into solution and to be absorbed onto the paper. This gives a record of the spray, which can then be used for comparison purposes.
The amount of net contents is determined by weighing full containers, dispensing the contents, then reweighing the container. The difference in weight gives the net weight.
Foam stability can be determined using a number of tests. The foams may be quick breaking or they may remain stable for one hour or more depending on the formulation. The stability can be determined by visual examination, by determining the time taken for a given mass to penetrate the foam, time taken for a given rod that has been inserted into the foam to fall or by using rotational viscometers.
Particle size is determined using cascade impactor (Figure 12.18). The test is done by carrying particles in a stream of air through a series of consecutively smaller jet openings. The bigger and higher density particles get impacted on the slide under the larger openings. As the stream proceeds, the openings get smaller and thus the smaller or the less dense particles are deposited on the progressive slides.
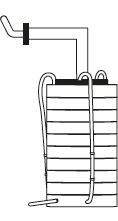
Figure 12.18 Image of a Cascade Impactor
The leak test determines whether the valve crimping is free from any leakage. The test can be accomplished by determining the dimensions of the crimp in metal containers and ensuring that it meets the required specifications. After filling the aerosols into the containers, a final leak test is performed by passing the filled containers through heated water baths. The containers are carried by a magnetized chain and submerged into the water bath. The container travels in the water bath such that, by the time it emerges out of the bath, the temperature of the product should reach 130°F. The container should not show any evidence of leakage or distortion.
Leave a Reply