When a fatty acid is attached by an ether linkage rather than by an ester linkage, at carbon 1 of the core glycerol molecule, a plasmalogen is produced. For example, phosphotidyl ethanolamine is the plasmalogen that is similar in structure to phosphotidyl ethanolamine.
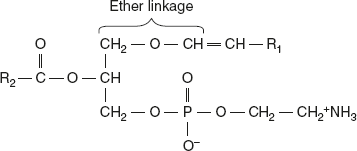
Myelin contains large amount of ethanolamine plasmalogen, and heart muscle contains large amounts of choline plasmalogen. Plasmalogen constitutes as much as 10% of the phospholipids of brain and muscle. Typically, the alkyl radical is an unsaturated alcohol. In some instances, choline, serine, or inositol may be substituted for ethanolamine.
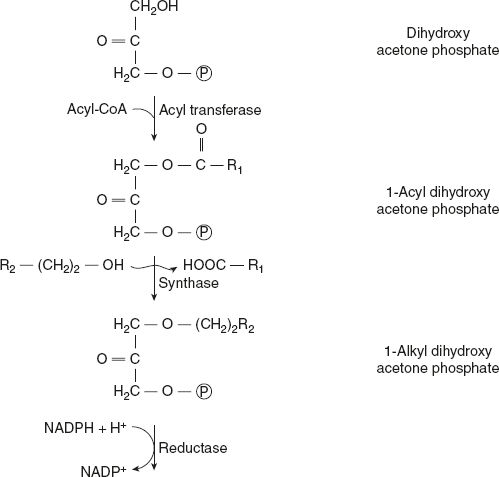
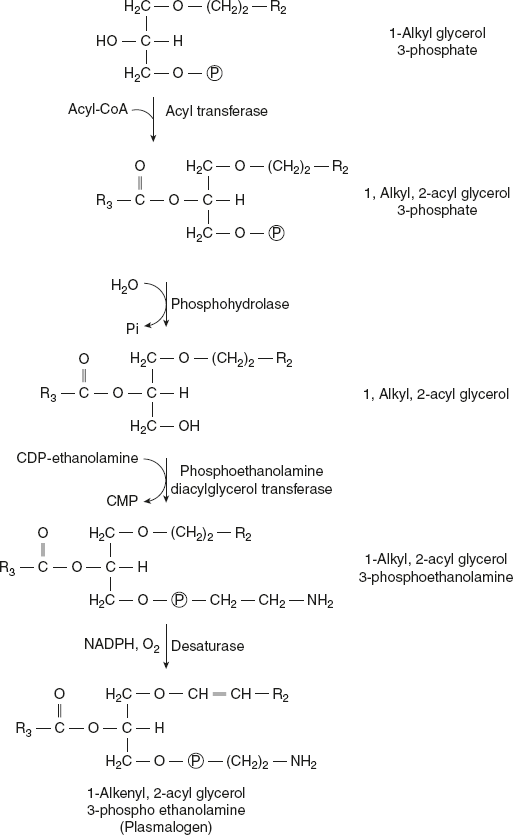
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is the precursor of glycerol ether phospholipids. This compound combines with acyl-CoA to give 1-acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate. An exchange reaction takes place between the acyl group and a long chain alcohol to give a 1-alkyldihydroxyacetone phosphate, which, in the presence of NADPH, is converted to 1-alkyl glycerol 3-phosphate. After further acylation in the 2 position, the resulting 1-alkyl, 2-acyl glycerol 3-phosphate is hydrolysed to give the free glycerol derivatives.
Plasmalogens are formed by the desaturation of the analogues 3-phosphoethanolamine derivative. Most of the phospholipid in mitochondria consist of plasmalogen.
Leave a Reply