The primary structure of protein refers to the number sequence of amino acids and the constituent units of polypeptide chain. The main mode of linkage of amino acids in proteins is the peptide bonds which link the α-carboxyl group of amino acid residue to the α-amino group of the other.
Linus Pauling and Robert Corey in the late 1930s demonstrated the α-carbon of adjacent amino acids, which are separated by three covalent bonds arranged as Cα—C—C—Cα This is as shown in Figure 3.4.
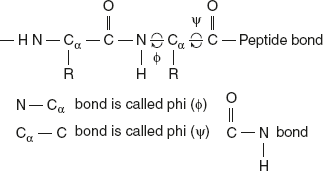
Figure 3.4 Structure of Bond in Peptide
Rotation is permitted around the bond between nitrogen and α-carbon atom of the main chain (N—Cα) and between the α-carbon atoms and carbonyl atoms (Cα—C).
Leave a Reply