Pyrimidine ring is first synthesised and then attached to ribose 5-phosphate. This is in contrast to purine nucleotide synthesis, where in purine, the ring is built upon a preexisting ribose 5-phosphate.
Glutamine transfers its amido nitrogen to CO2 to produce carbamoyl phosphate. This reaction is ATP dependent and is catalysed by cytosol enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II).
CPS II is activated by ATP and PRPP and inhibited by UTP. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I) is a mitochondrial enzyme which synthesises carbamoyl phosphate from ammonia and CO2 and in turn urea. Carbamoyl phosphate condenses with aspartate to form carbamoyl aspartate. This reaction is catalysed by aspartate transcarbamoylase. Dihydroorotase catalyses the pyrimidine ring closure with a loss of water. The three enzymes (CPS II, aspartate transcarbamoylase, and dihydroorotase) are the domains (functional units) of the same portion. This is a multifunctional enzyme. The next step in pyrimidine synthesis is an NAD+-dependent dehydrogenation, leading to the formation of orotate. Ribose 5-phosphate is now added to orotate to produce uridine monophosphate (OMP). This reaction is catalysed by orotate phosphoribosyl transferase, an enzyme comparable with HGPRT in its function. OMP undergoes decarboxylation to uridine monophosphate (UMP). Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase and OMP decarboxylase are domains of a single protein. By an ATP-dependent kinase reaction, UMP is condensed to UDP, which serves as a precursor for the synthesis of dUMP, dTMP, UTP, and CTP. Ribonucleotide reductase converts UDP to dUDP by a thioredoxin-dependent recrimination; thymidylate synthetase catalyses the transfer of a methyl group from N5, N10 methylenetetrahydrofolate to produce deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). UDP undergoes an ATP-dependent kinase reaction to produce UTP. Cytidine triphospahte (CTP) is synthesised from UTP by amination. CTP synthetase is the enzyme and glutamine provides the nitrogen. Thus, the pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesised from UMP as described in Figure 11.7.
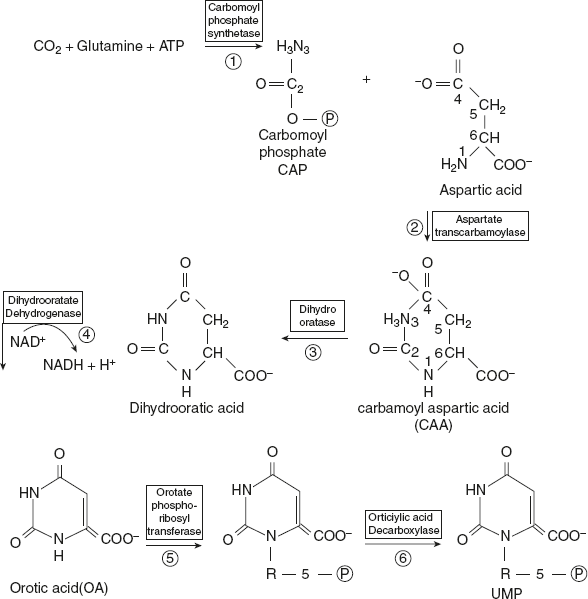
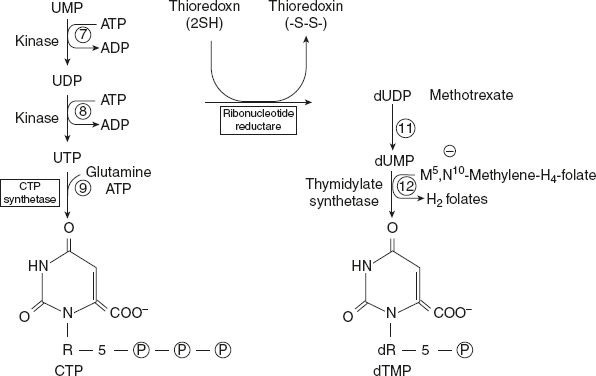
Figure 11.7 Synthesis of Pyrimidine Nucleotides
Leave a Reply