Arthur Kornberg in 1955 discovered the enzyme DNA polymerase from E. Coli for the synthesis of nucleotides as shown in Figure 5.5.
DNA polymerase is 109 Kdal single polypeptide chain. It catalyses the step-by-step addition of polynucleotide units to a DNA chain.
(DNA)n residues + dNTP ![]() (DNA)n+1 + PPi
(DNA)n+1 + PPi
DNA polymerase requires the following components to synthesis DNA chain.
All four deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphate dATP, dGTP, dTTP, and dCTP must be present. DNTP used to refer these deoxynucleoside triphosphate-Mg2+ is also required.
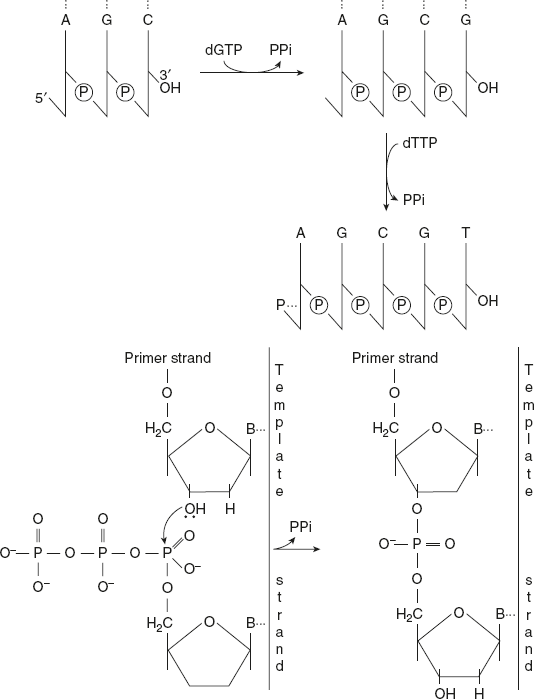
Figure 5.5 DNA Polymerase Catalyses Elongation of DNA Chain in the 5′-3′ Direction
DNA polymerase adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3′ hydroxyl terminus of a preexisting DNA or RNA. A primer chain with 3′-OH group is required.
A DNA template is essential. The template can be single- or double-stranded DNA.
Chain elongation reaction catalysed by DNA polymer occurs by means of a nucleophilic attack of the 3′–OH terminus of the primer on the innermost phosphate atom of the incoming deoxynucleoside triphosphate.
A phosphodiester bond is formed, and pyrophosphate is concomitantly released. The subsequent hydrolysis of pyrophosphate drives the polymerisation forward. This displacement of the overall equilibrium could not occur if the activated intermediate were nucleoside diphosphate.
The elongation of DNA chain proceeds from 5′ to 3′ direction. About ten nucleotides are added per second per molecule of DNA polymerase l.
Polymerisation is processive; that is, many nucleotides are added without the release of the enzyme from the template.
DNA polymerase catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bond only if the base on the incoming nucleotide is complementary to the base on the template strand. Thus, DNA polymerase is a template-directed enzyme.
Leave a Reply